A canonical URL tells search engines which version of a blog post is the original one. It prevents duplicate content, keeps your site organized, and makes sure Google ranks the right page. By setting a canonical tag, you guide search engines to your preferred URL so your blog keeps its SEO strength in one place.
Thank you for reading this post, don't forget to subscribe!What Is a Canonical URL?
A canonical URL is the “preferred” version of a webpage that you want search engines to index. It tells search engines:
“This is the official version of this page. ”This is important when you have duplicate or similar content across multiple URLs.
You have several URLs showing the same product:
- /shirt?color=blue
- /shirt?size=medium
- shirt/blue
A canonical tag points to the URL you want Google to count as the main page:
<link rel=”canonical” href=”https://www.example.com/shirt” />
What Is a URL?
A URL (Uniform Resource Locator) is the address of a webpage. It’s what you type into a browser to visit a website. It’s one of the basic building blocks of on-page SEO. It plays a big role in user experience and how search engines understand your website.
Example:
A URL tells both users and search engines where a page lives on your site
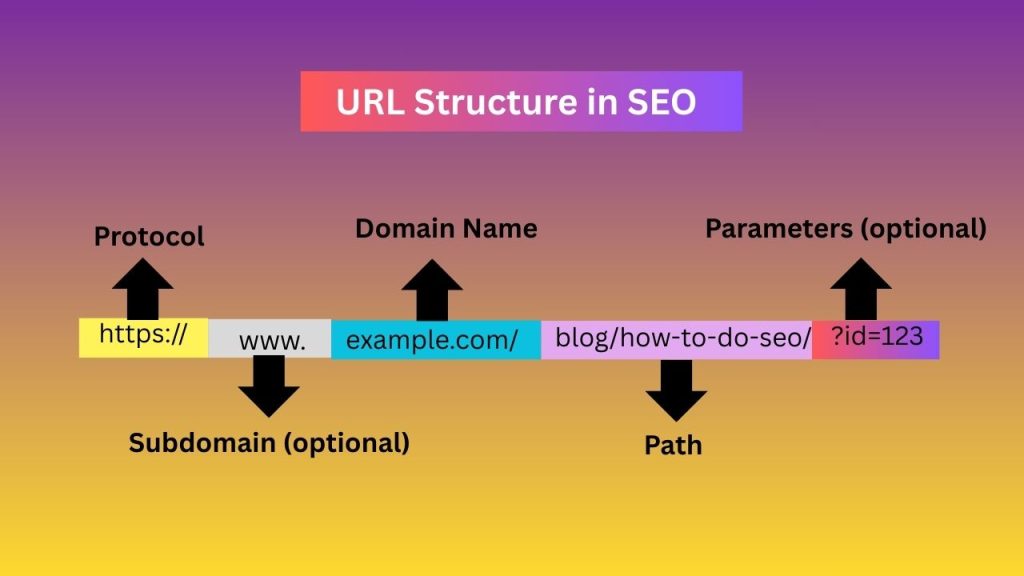
Parts of a URL
- Protocol – https://
Shows the connection type. HTTPS is secure and preferred by Google. - Domain Name – example.com
The main address of the website. - Subdomain (optional) – www.
A section of your website, such as blog.example.com. - Path – /blog/how-to-do-SEO
The location of a specific page. - Parameters (optional) – ?id=123
Often used for tracking or dynamic pages. Best to avoid SEO unless necessary.
Canonical URL vs 301 Redirect
| Feature | Canonical URL | 301 Redirect |
| Purpose | Tells Google which version of similar pages is the preferred one | Permanently moves users and search engines to a new URL |
| User Redirect? | ❌ No | ✅ Yes |
| Page Removed? | ❌ No, all versions stay live | ✅ Yes, old page becomes inactive |
| Google Signal Strength | Medium (a hint) | Strong (a directive) |
| Best For | Duplicate pages that must stay online | Pages you want to delete, replace, or merge |
| SEO Value Transfer | Partial / depends on Google | Full SEO value passed to the new URL |
| Use Case in Blogs | Tag pages, UTM links, similar versions | Merging old posts into a new updated post |
| Use Case in E-commerce | Filters (size, color), sorting URLs | Discontinued products, outdated URLs |
| Keeps Multiple URLs Active? | ✔ Yes | ❌ No |
| Prevents Duplicate Content? | ✔ Yes | ✔ Yes |
| Affects Site Navigation? | ❌ No | ✔ Yes |
| Technical Complexity | Easy to set | Moderate (requires server or CMS settings) |
| Example | Keep /shirt?color=blue, but tell Google /shirt is main | Redirect /old-blog-post → /new-blog-post |
Fixing Duplicate Content With Canonicalization
If you have 4 different URLs showing the same content, Google sees them as duplicate pages. This can hurt your SEO because:
- Google doesn’t know which URL to index
- Ranking power gets split between the duplicate URLs
- Crawl budget gets wasted
The best solution is canonicalization — choosing one URL as the “main” page.
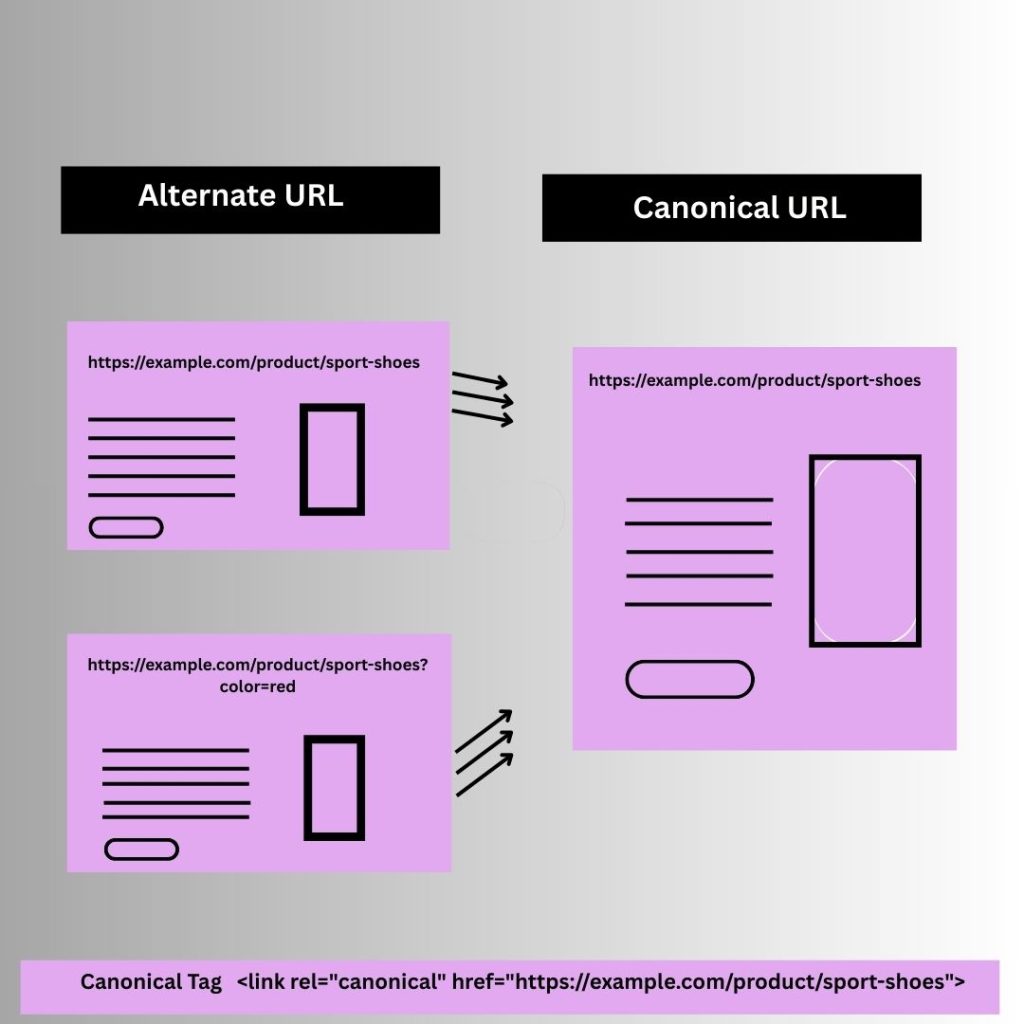
For example:
Imagine you have a product page for a pair of sports shoes.
4 Alternate URLs:
- https://example.com/product/sport-shoes
- https://example.com/product/sport-shoes?color=red
- https://example.com/product/sport-shoes?ref=homepage
- https://example.com/product/sport-shoes?size=9
If https://example.com/product/sport-shoes is the main product page, the canonical tag <link rel=”canonical” href=”https://example.com/product/sport-shoes”> should be added to all duplicate pages to indicate that this is the preferred version for indexing.
Result
- All duplicate URLs point to a single preferred page.
- Google treats the canonical URL as the primary page for ranking.
- All ranking signals (links, authority, etc.) are consolidated into the canonical page.
This is exactly how canonicalization works. Why it’s good for SEO: It prevents duplicate content issues and ensures your main page gets the full SEO benefit.
What is a self-referencing canonical?
A self-referencing canonical is when a page points to itself in its canonical tag. For example:
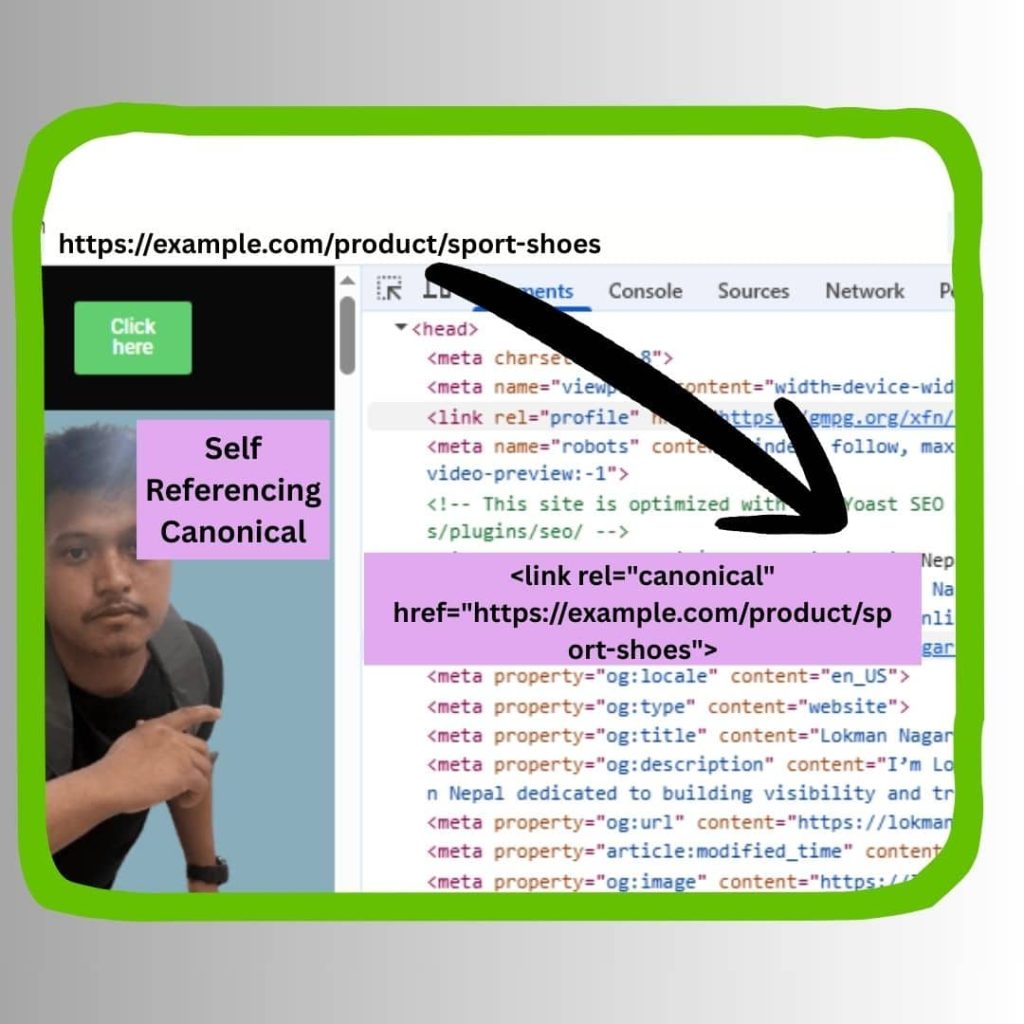
Here, the page sport-shoes is telling search engines: “This is the preferred version of this content,” even if it doesn’t have duplicates yet.
How to Optimize Canonical URLs in SEO
- Add a canonical tag to every page
- Point canonicals to the main version of the page
- Avoid self-canonical errors
- Use 301 redirects when necessary
- Keep consistent internal links
What This Canonical Tag Does
- 1. Prevents duplicate content: If Google finds duplicates or tracking parameters, it will still choose this page.
- 2. Combines ranking signals: Backlinks, engagement, and metrics from other versions will be credited to this URL.
- 3. Sends a strong signal: “It’s this page—not any variation—that should rank.”
- 4. Protects your SEO: Avoids split ranking and confusion for Google’s crawlers.
